Energy Landscapes - Beyond the Operational
Introduction
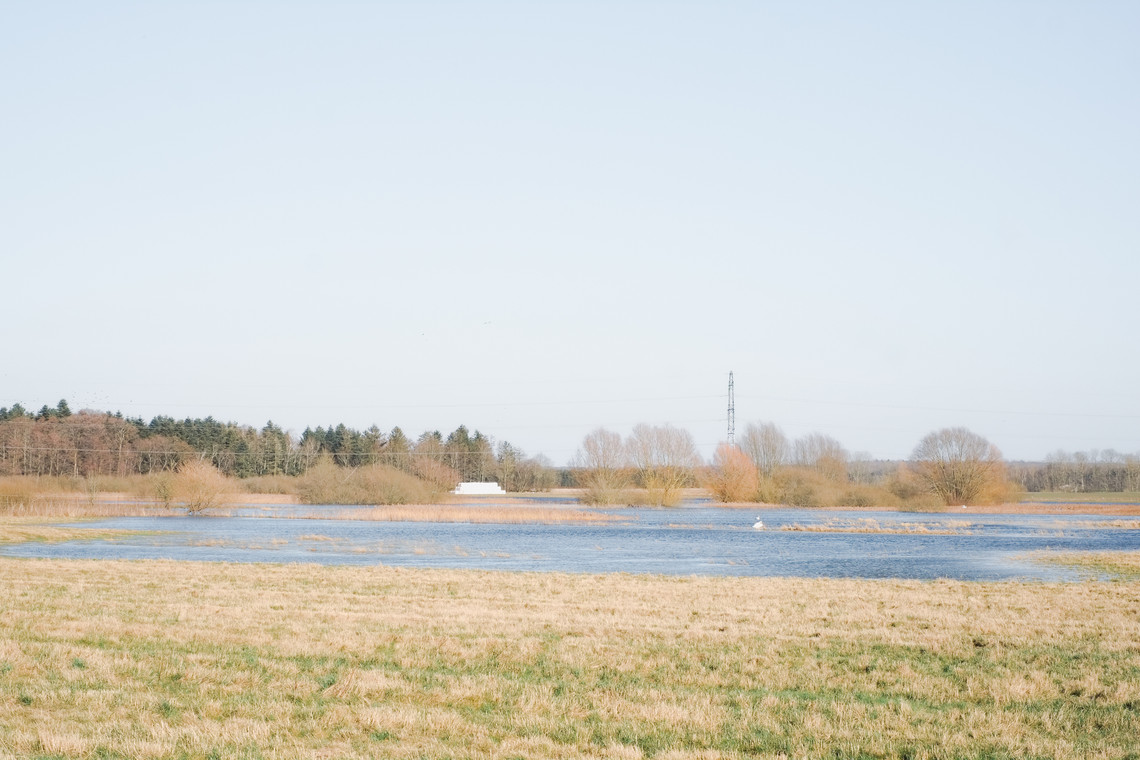
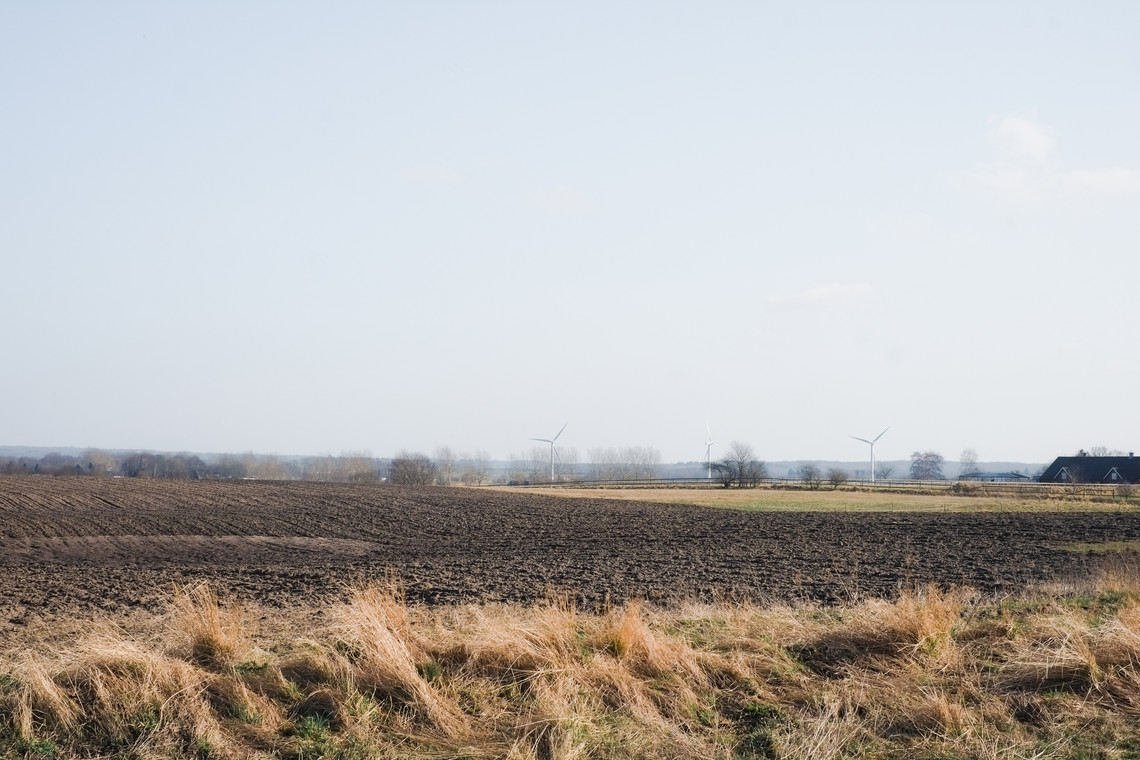
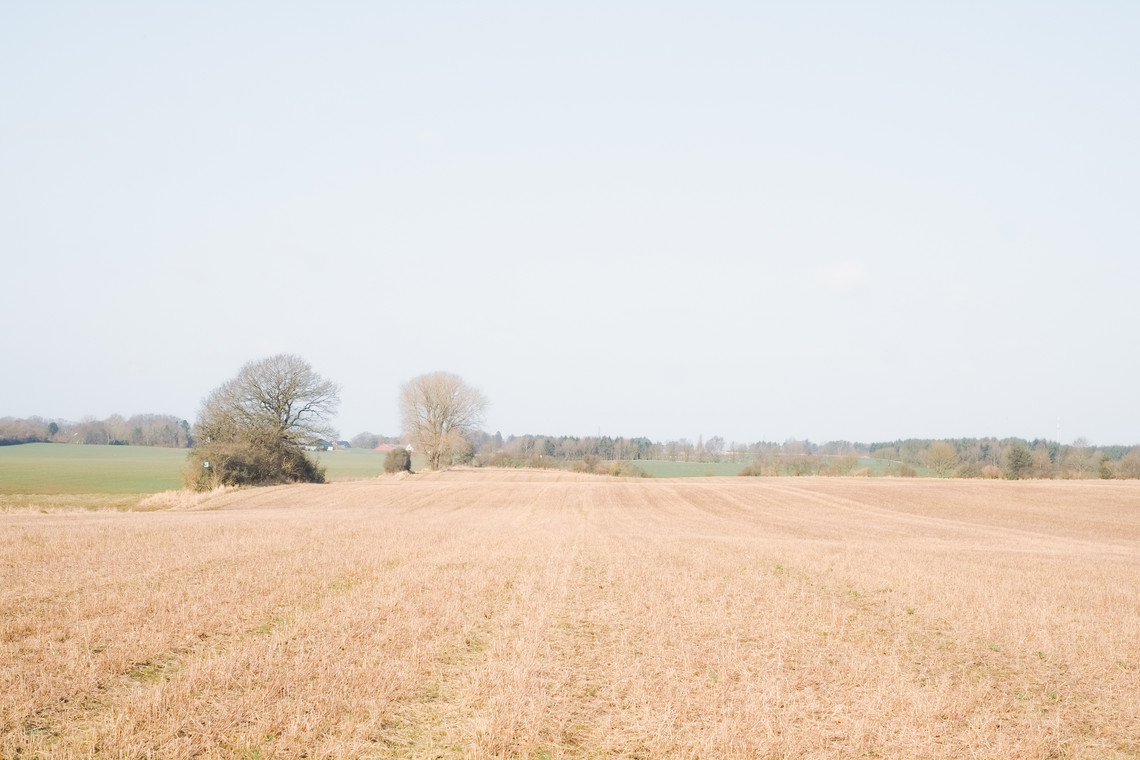
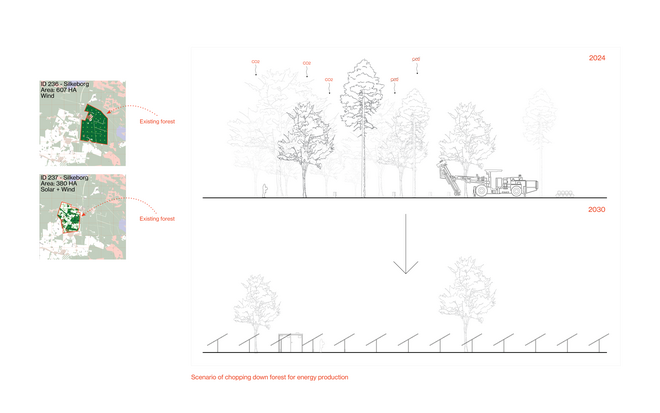
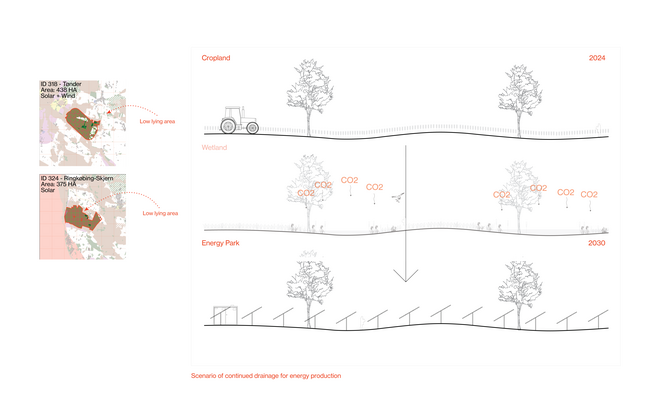
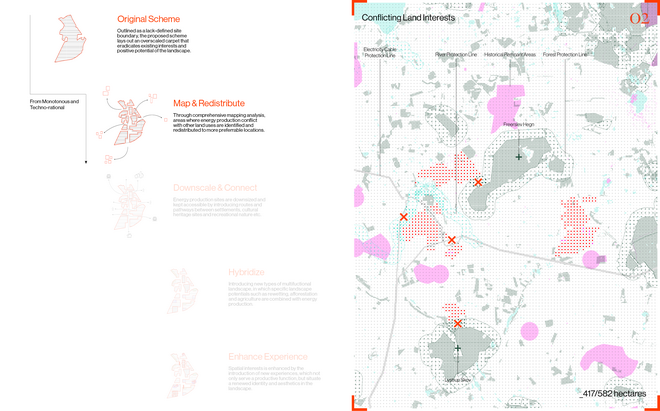
As we approach decarbonization, energy transitioning becomes a cornerstone of our efforts. However, infrastructures of renewable energy, just like those of fossil fuels, exploit space as a resource. This puts increased pressure on the hinterland – which among other interconnected crises around climate change, biodiversity, and food, it would be further burdened by the environmental costs of energy production. Although the hinterland has long been the productive back-of-house for the urban cores, it is set to undergo substantial transformation and disruption of existing spatial arrangements—from what was once remote and open, to increasingly closed and operational. Hence, the demand to expand renewable energy infrastructures necessitates negotiations among various land uses.
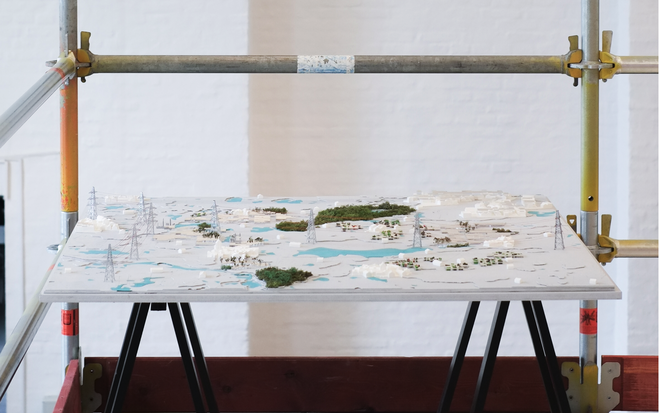
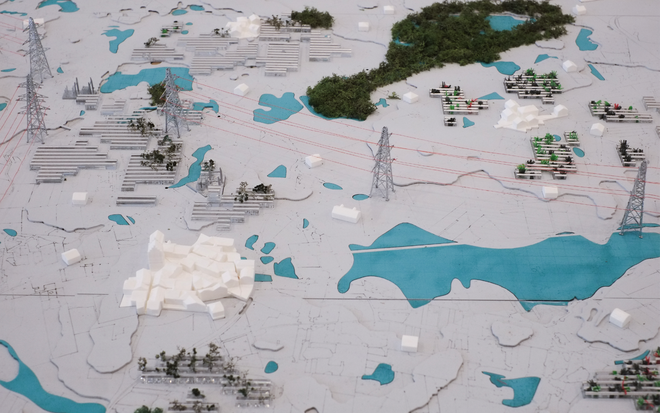
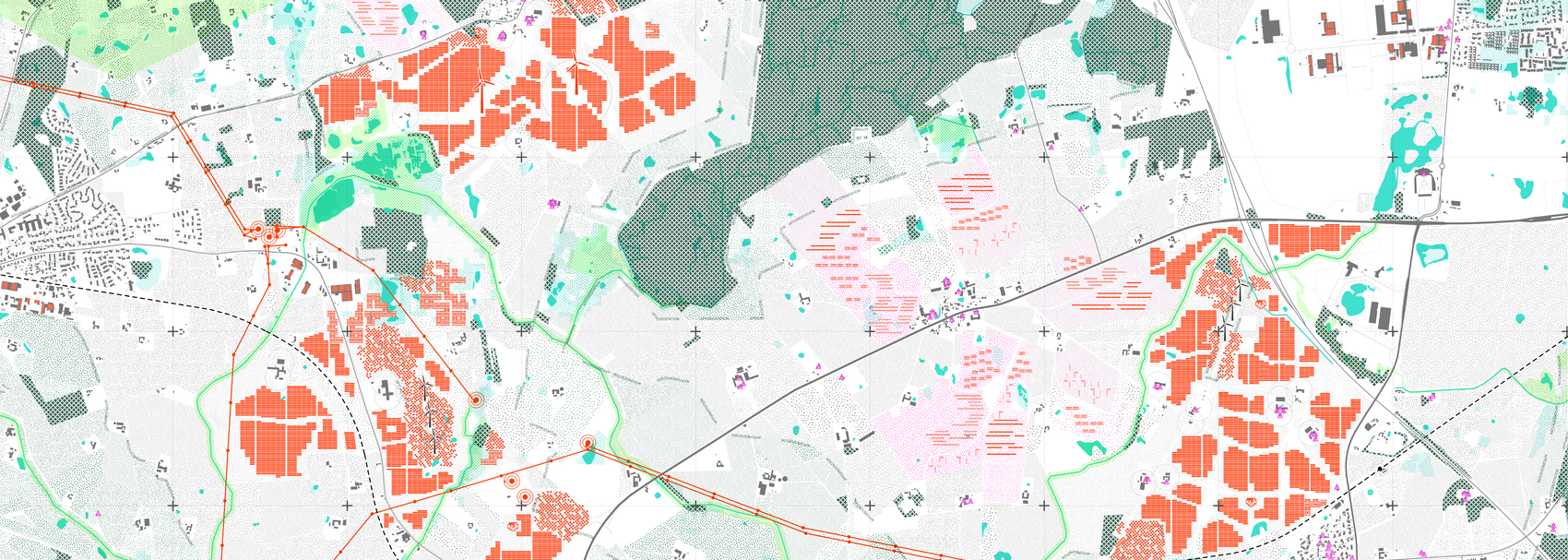
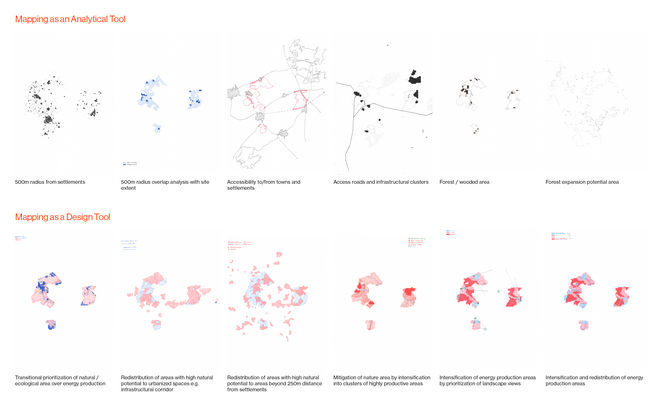
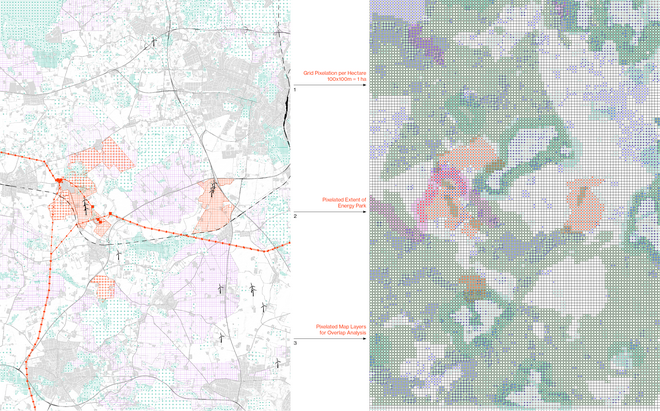
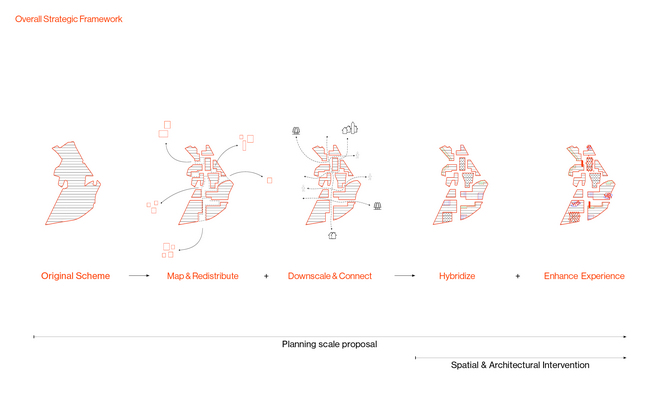
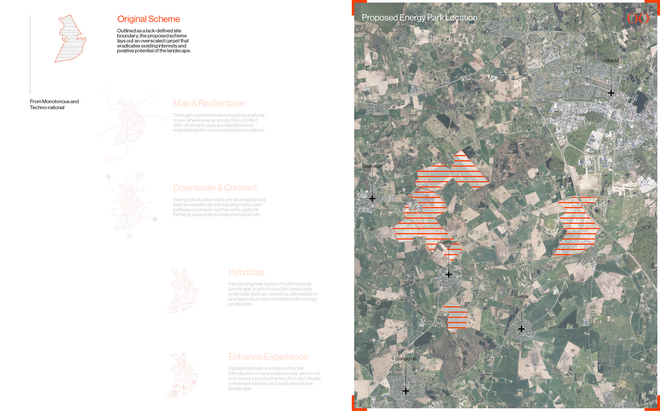
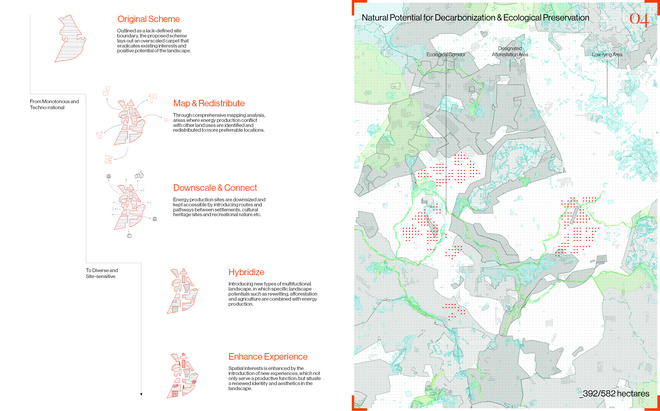
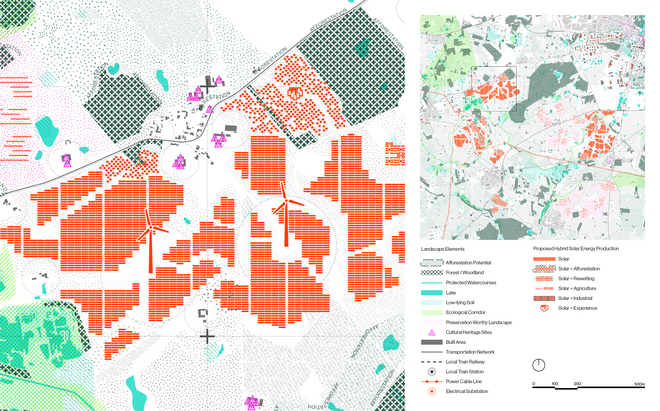
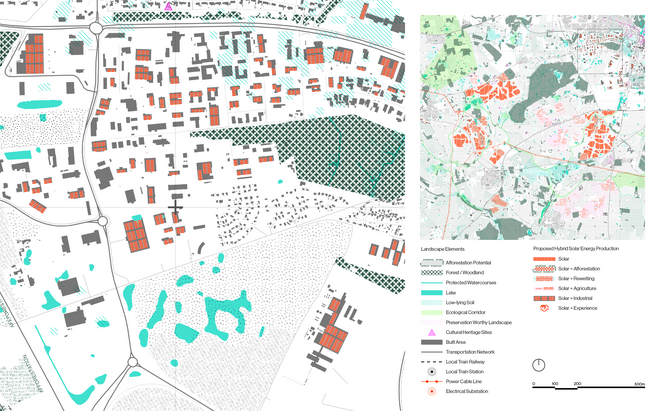
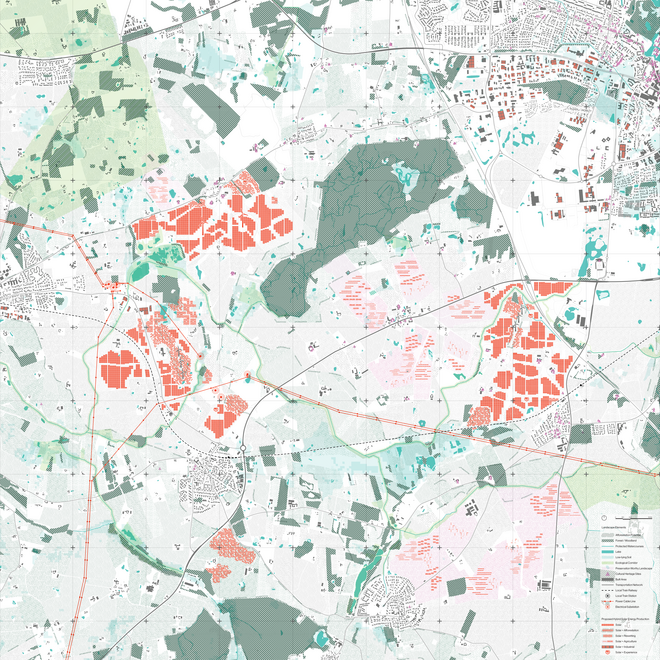
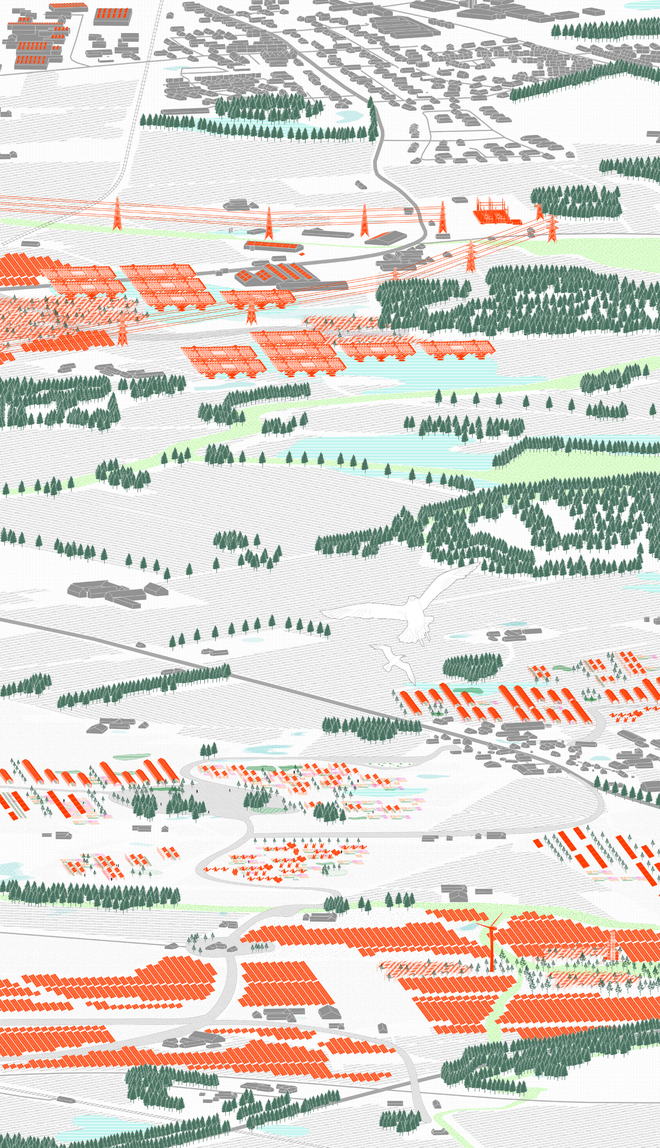
Energy Landscapes – Beyond the Operational departs from reflection on both the pressure and opportunities that energy transition brings to the rural landscape. The project proposes an alternative vision for planning and designing renewable energy parks in Denmark, specifically one of the suggested areas in the municipality of Hillerød. It challenges the predominant model of overly large and monotonous facilities that undermine sociocultural, ecological, and experiential values in rural landscapes. Instead, the project introduces a planning strategy that redistributes energy production to more suitable locations while hybridizing these spaces with landscape interests such as wetland restoration, afforestation, and agriculture. This approach explores new spatial configurations, experiences, and aesthetics of renewable energy production in coexistence with other valuable attributes of the rural landscape.
The project is made in collaboration with Victor Carlsen.
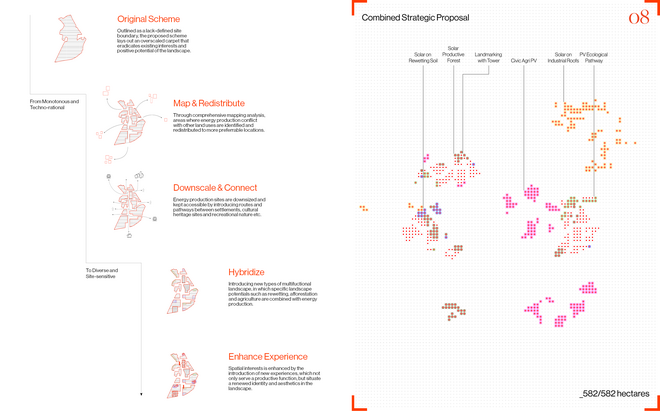
From Monotonous and Enclosed to Open and Diverse
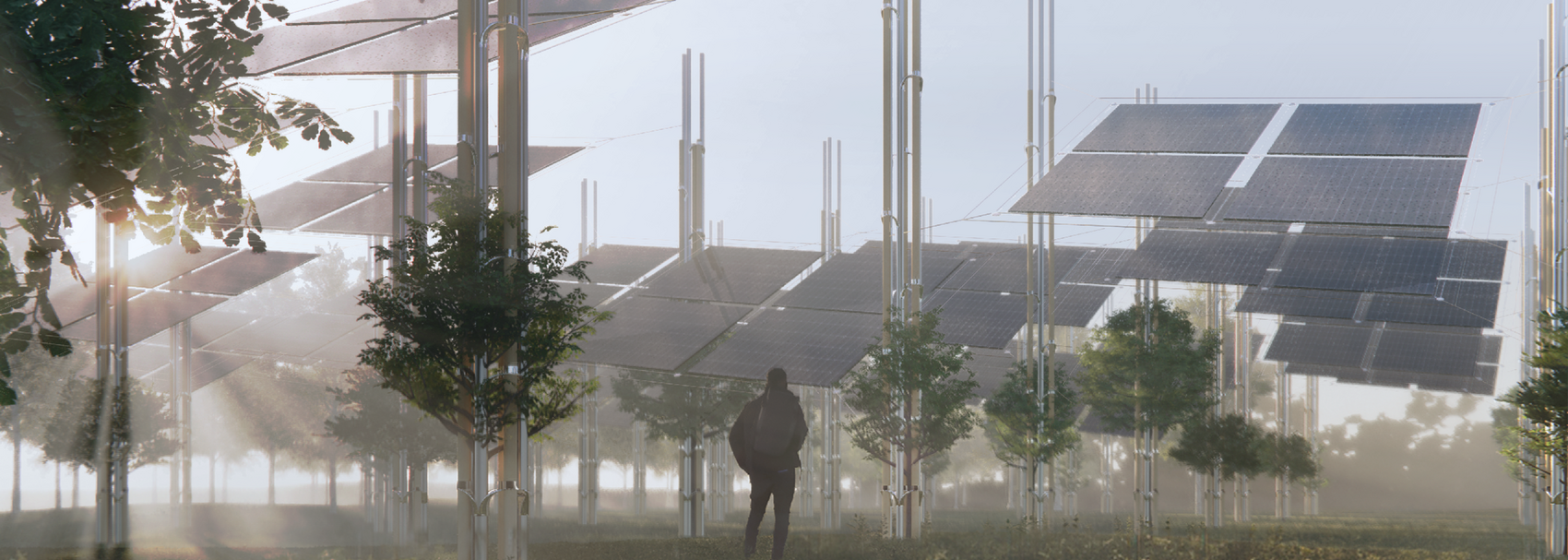
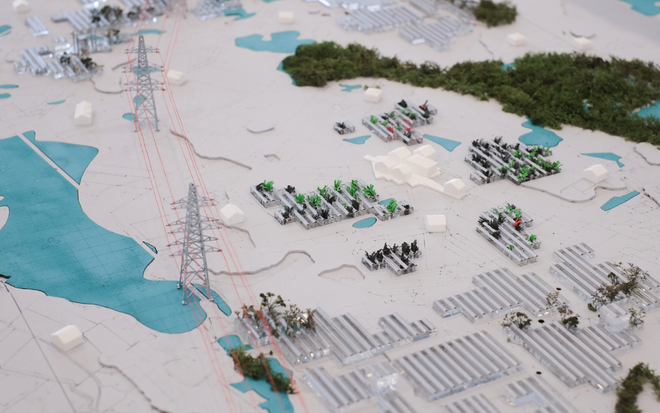
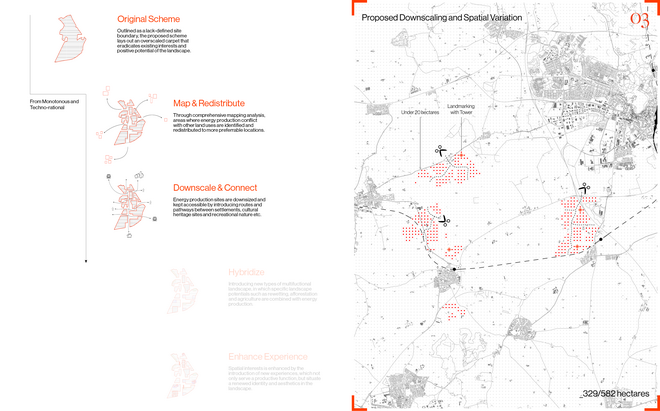
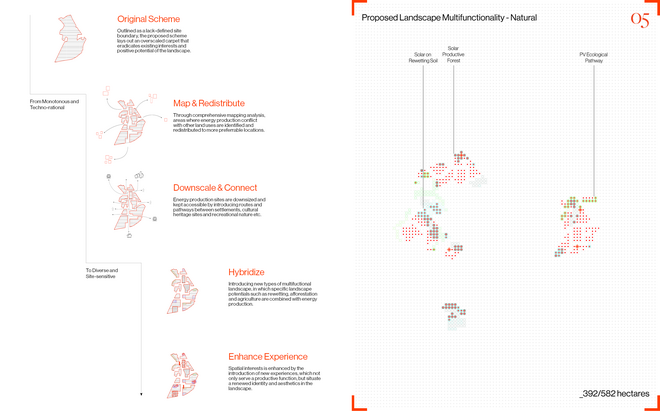
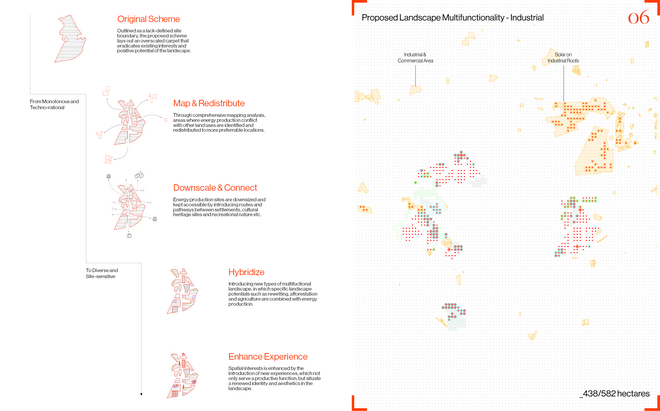
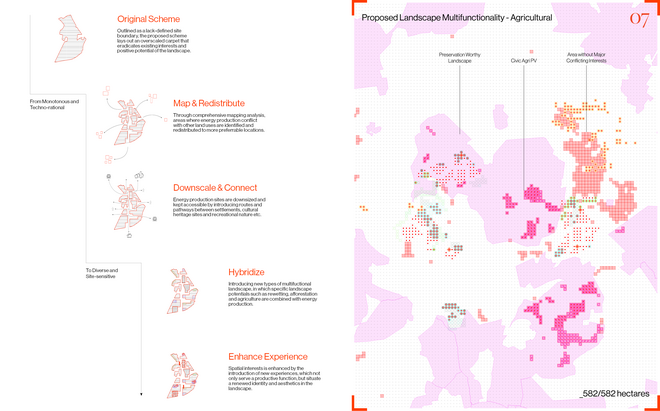
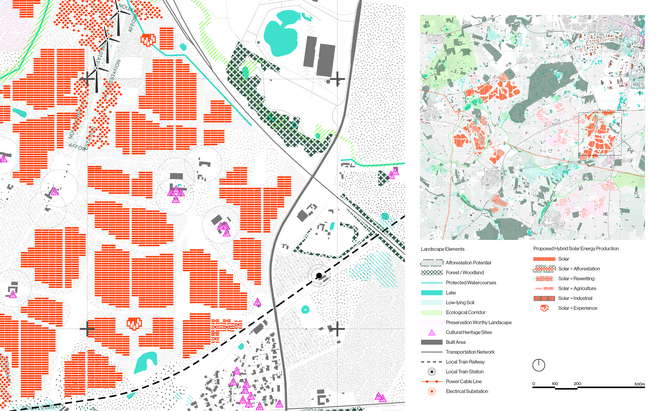
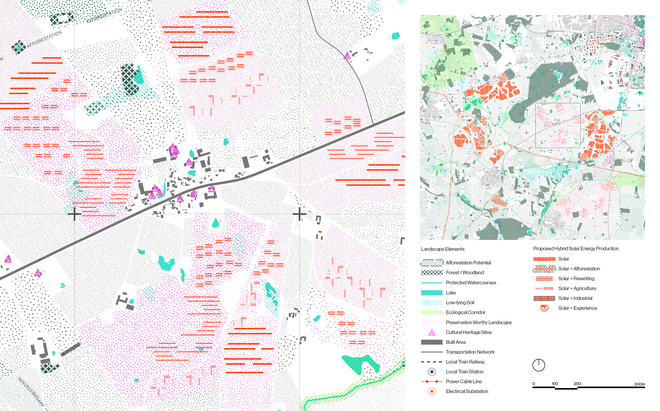
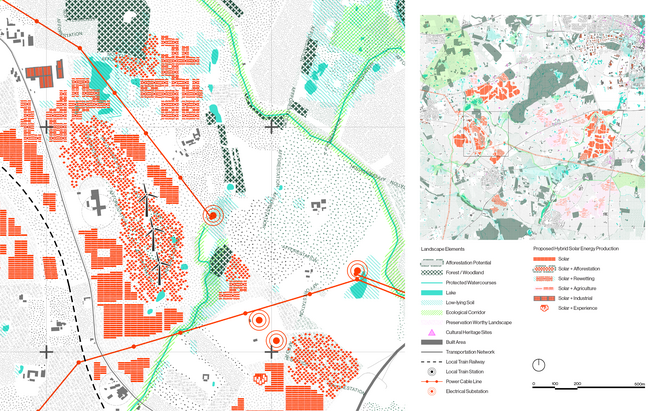
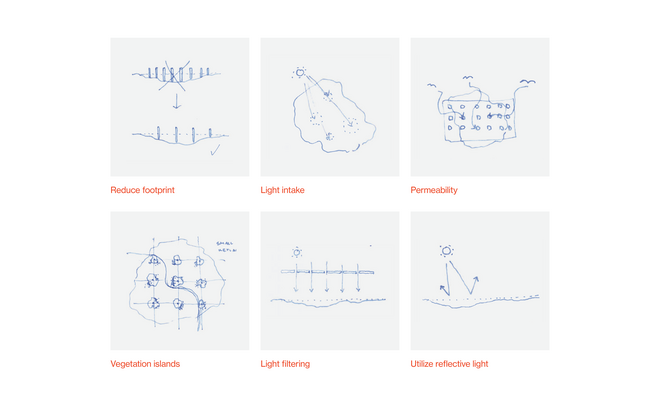
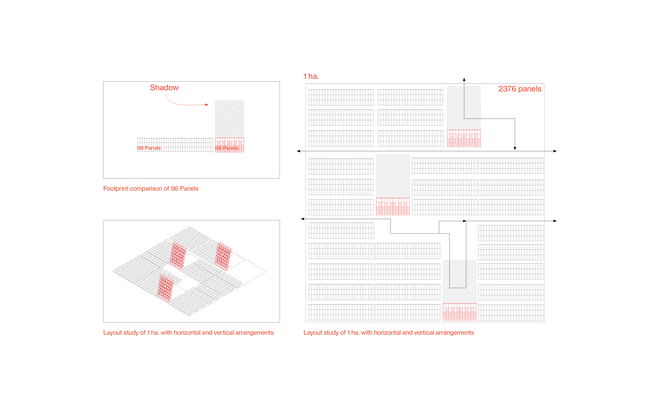
Driven by research empirics that Denmark would need 1.5 times of its area to achieve all its goals, the project advocates for multifunctionality in the planning of energy parks. By reimagining the design and organization of energy parks, we aim to produce models that are not only performative in terms of energy output, but also have the capacity to accommodate natural potential and respect the inherent qualities of the land. The interventions seek to shift away from a blanket of solar panels and look toward a mosaic landscape of diverse qualities through explorations of hybrid land use, new aesthetics, and spatialities.


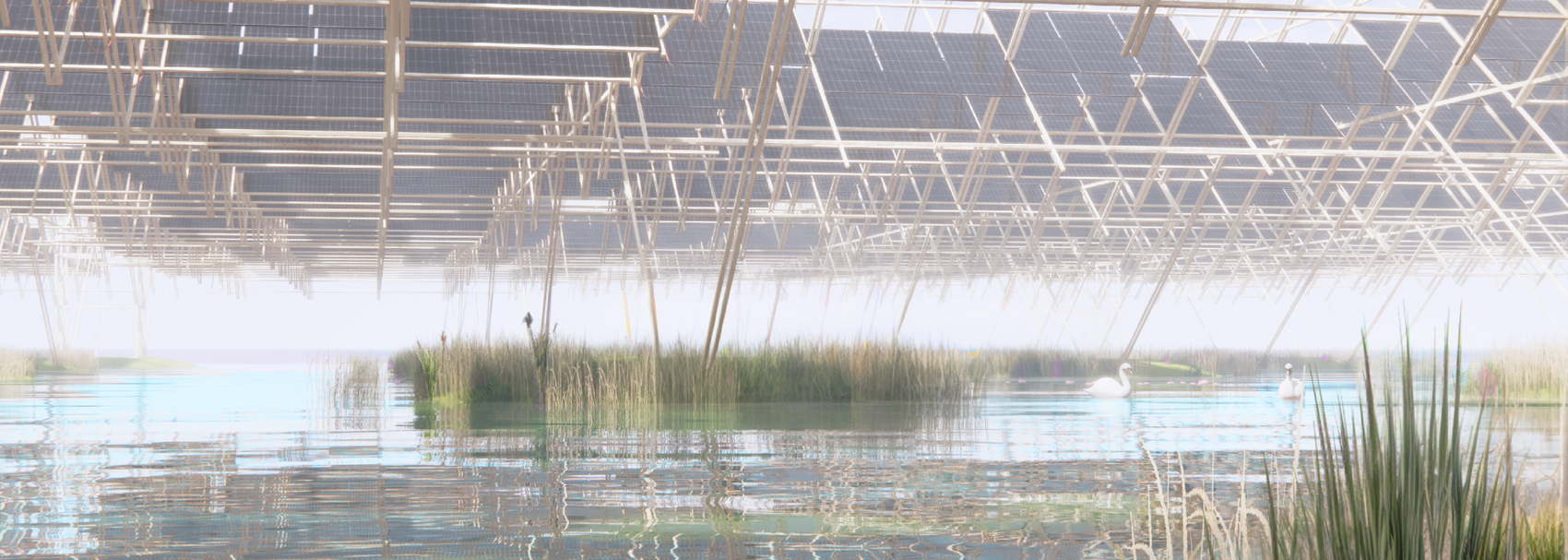
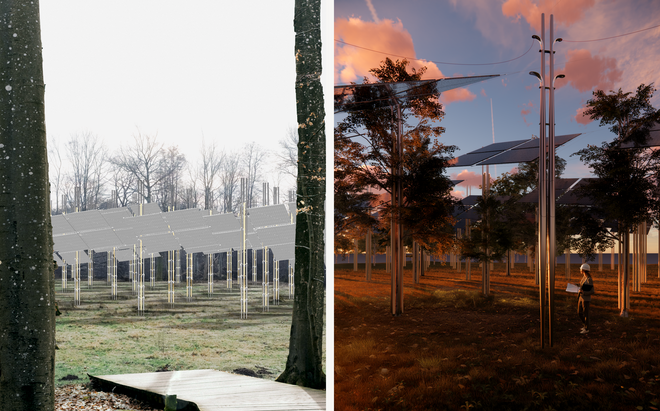
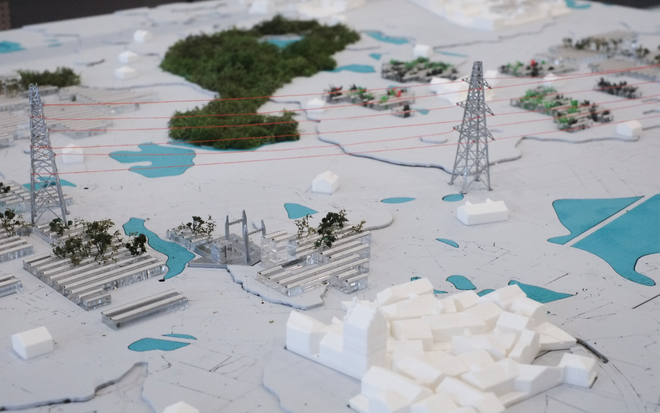
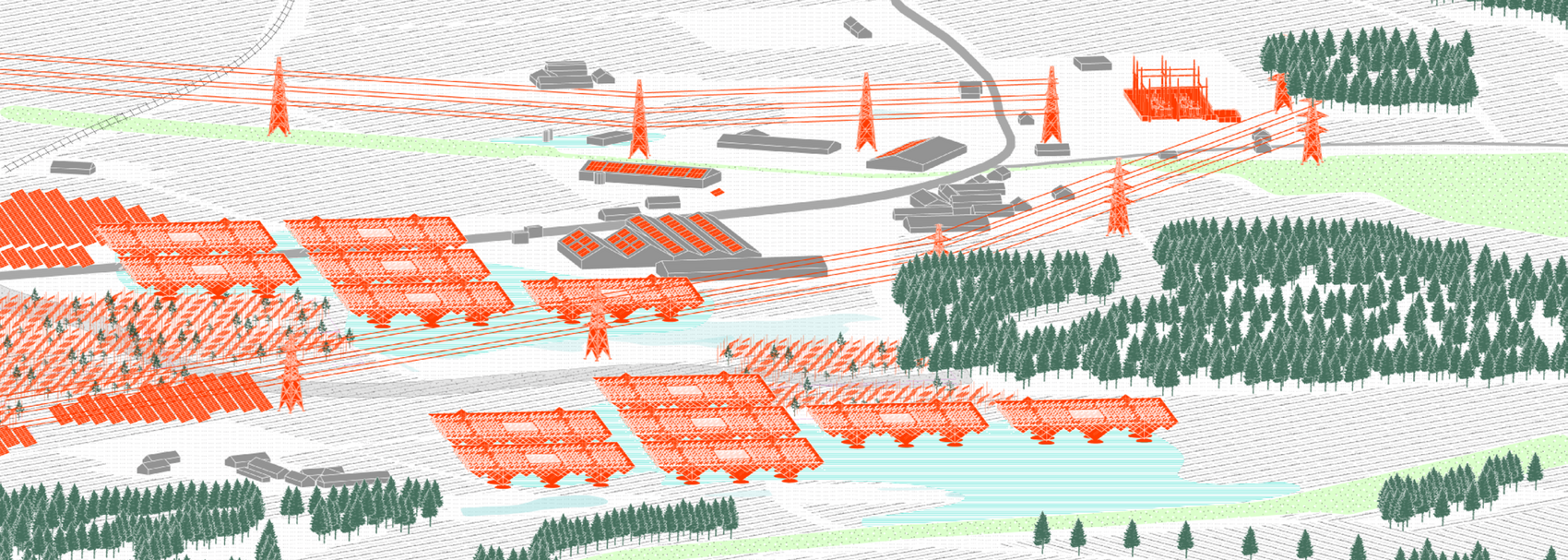
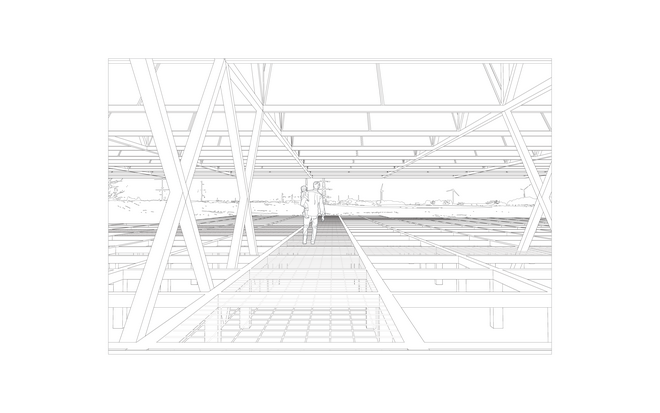
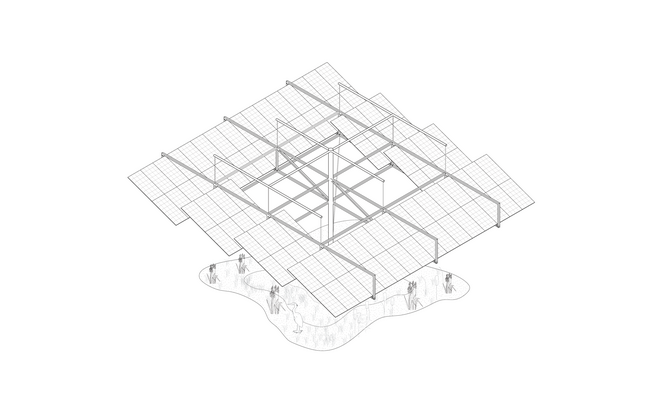
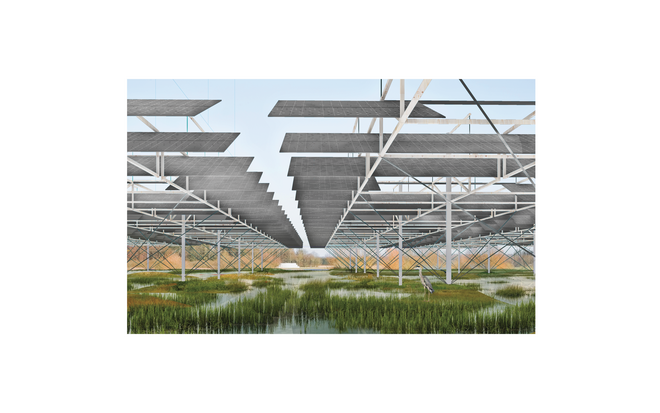
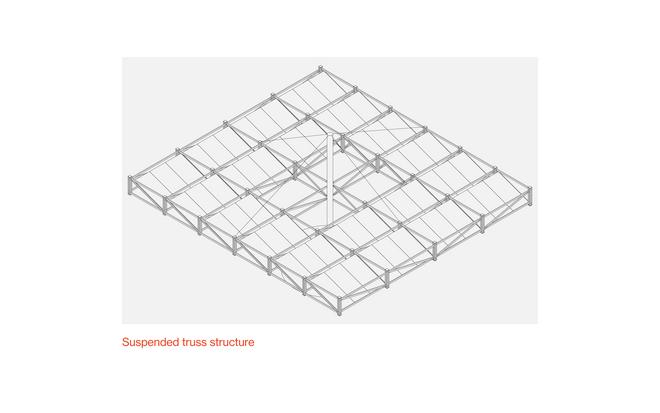
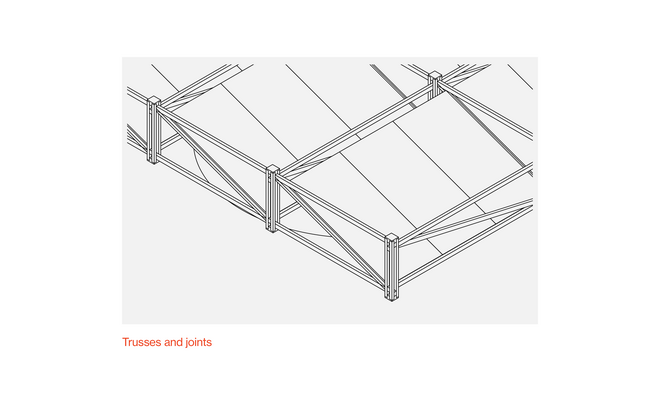
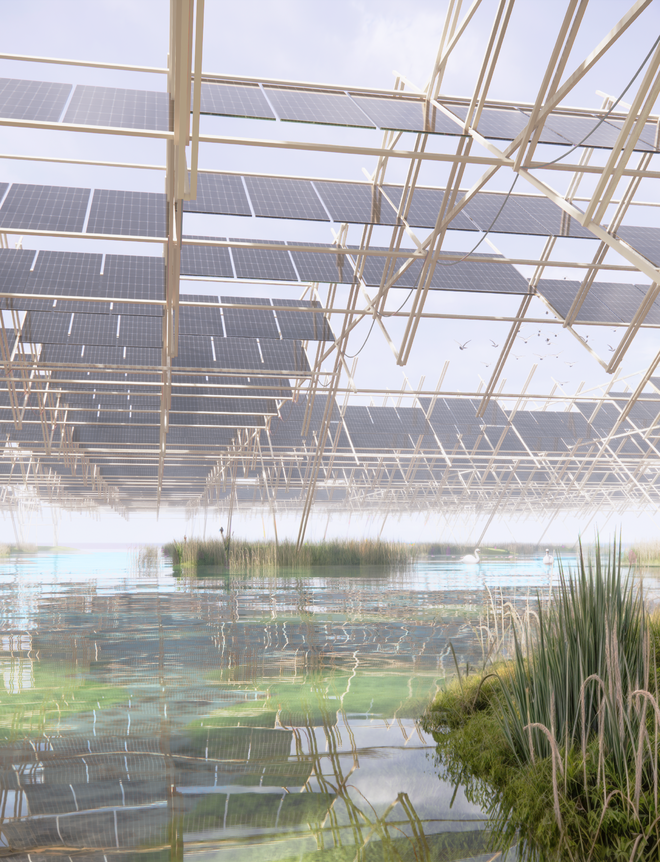
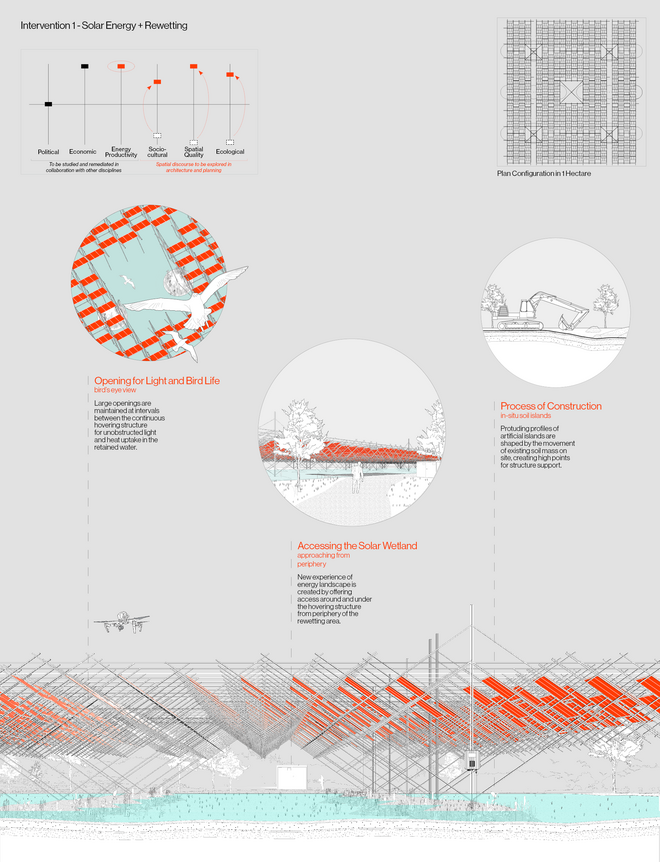
Solar + Rewetting
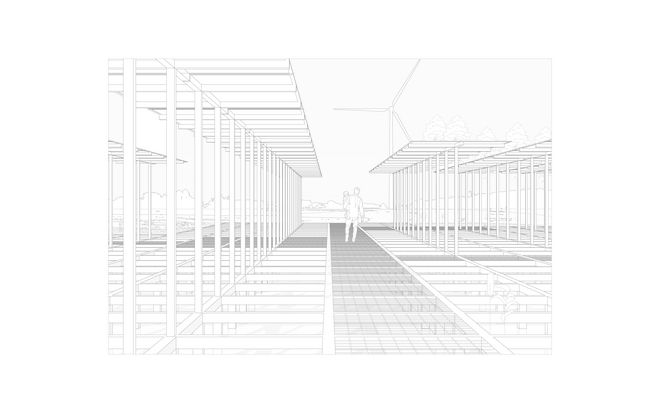
This intervention aims to utilize the natural potential of wetlands for water retention and carbon sequestration, with the addition of energy production as a secondary function. To achieve this, we explored the use of hovering structures that can accommodate the installation of solar panels without disturbing the landscape. The structural design is inspired by the configuration of solar panels, resulting in a framework that incorporates supportive diagonal elements, seemingly growing out of the landscape and landing on artificially constructed vegetated islands. Additionally, the structure features multiple openings to ensure proper light intake and accessibility to the wetland for birds. This approach creates a striking juxtaposition between highly artificial, technical elements and the natural environment.

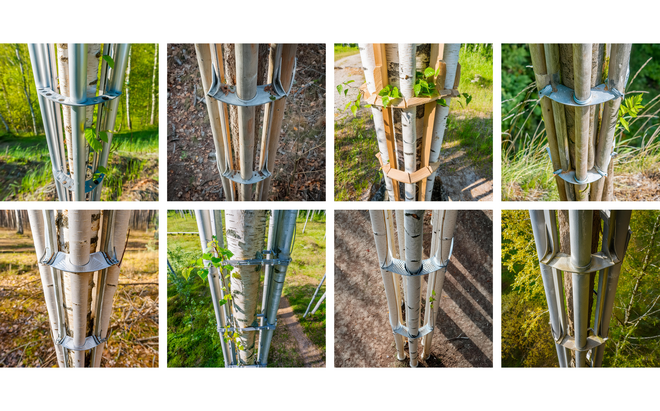
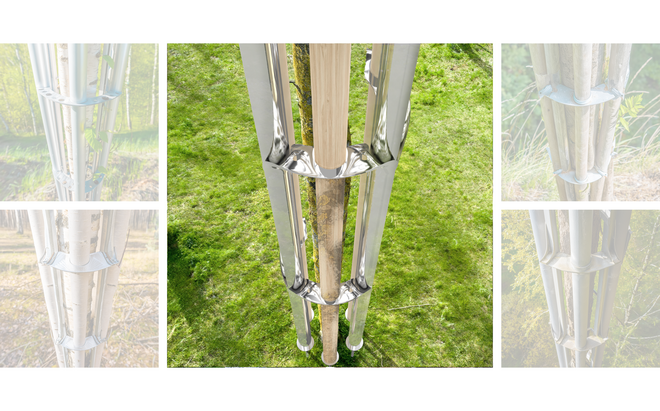
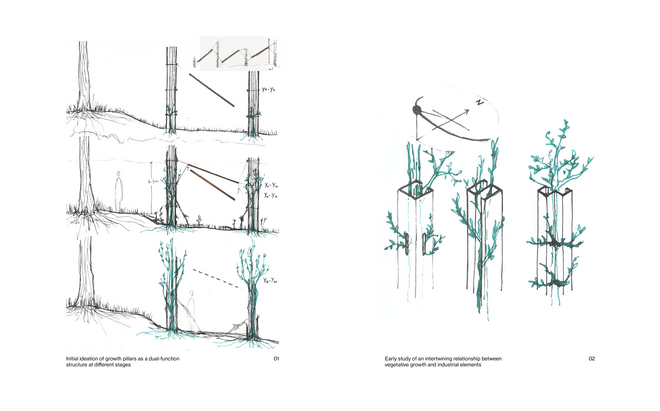
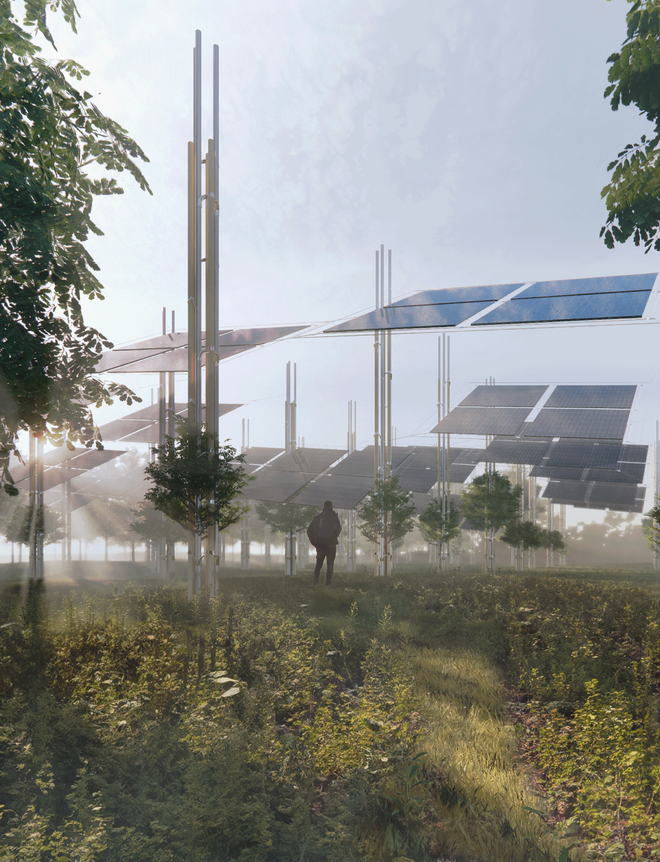
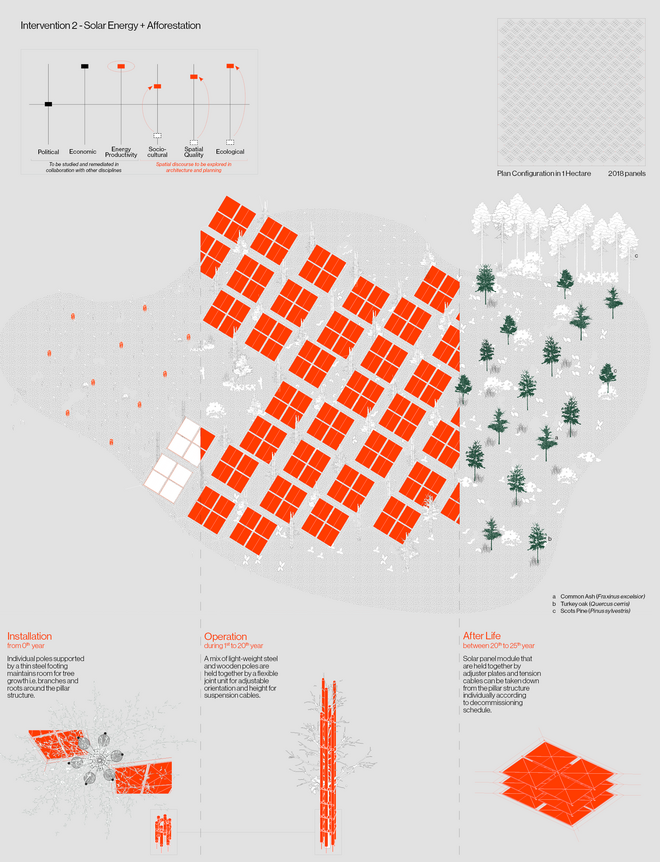
Solar + Afforestation
This intervention explores combining solar energy production with afforestation efforts. The design aims to promote the health and functionality of both solar panels and young trees through a bio-industrial hybrid structure. It envisions a framework that support the growth of tree saplings, while allowing elevated solar panels to be fixed among the pillars. This approach imagines a dynamic relationship between the bioprocess of carbon uptake from the atmosphere through photosynthesis in the trees and the temporality of harvesting energy from the sun for green electricity. Upon maturity, the system allows for either decommissioning and redistribution of the panels, leaving a forest in site for natural and cultural interest.

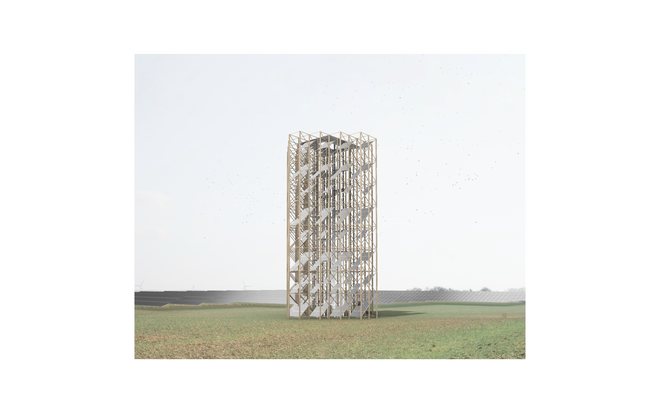
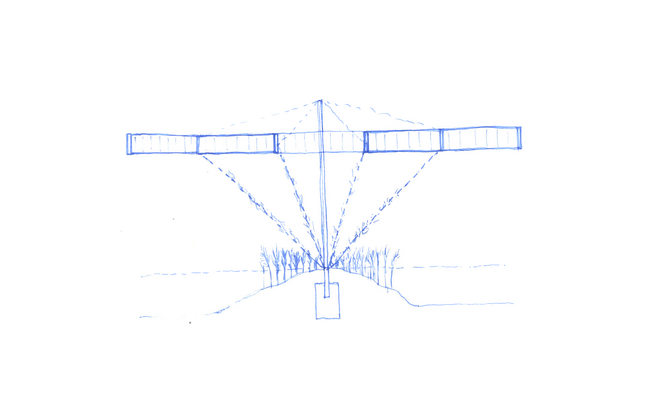
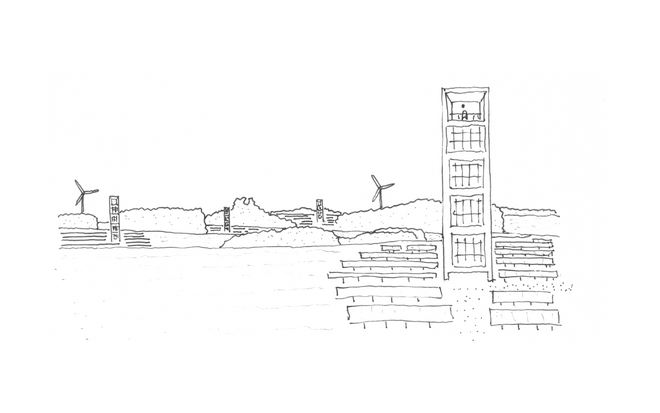
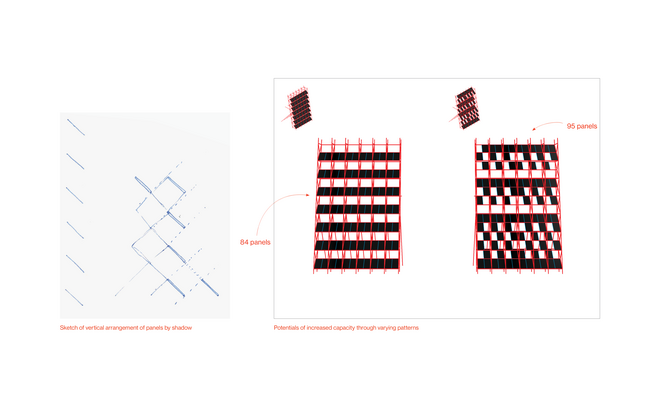
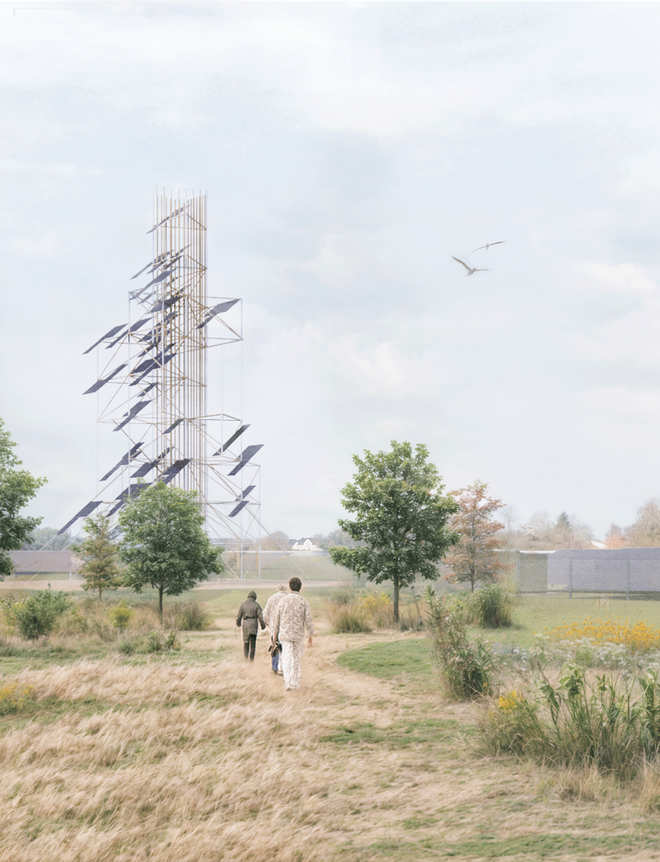
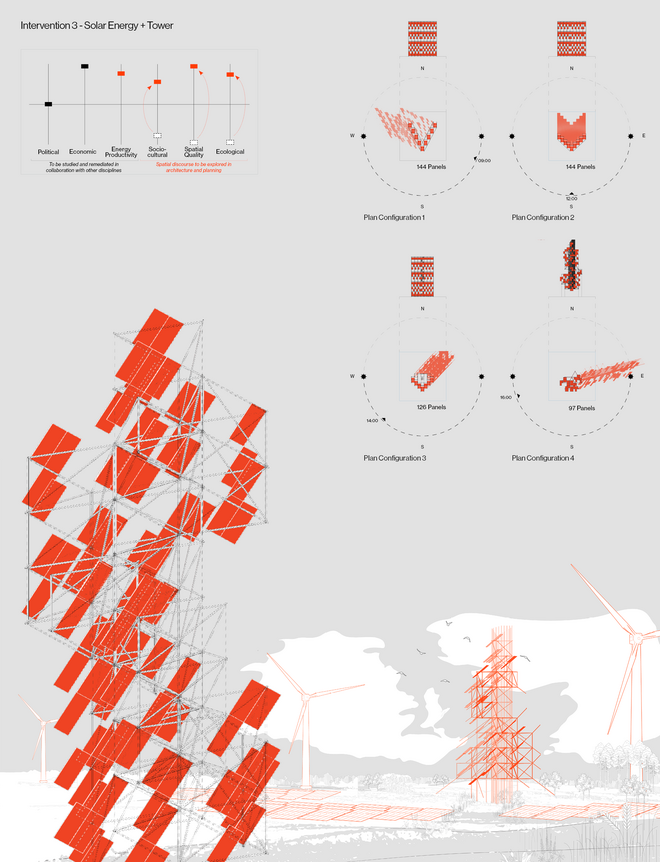
Solar + Tower
This intervention proposes a vertical arrangement of solar panels positioned on natural highpoints, drawing inspiration from iconic landmarks and watchtower structures. It aims to enrich the spatial diversity. The structure is based on a V-shaped design for even sunlight exposure, which through iterations is fragmented to impart a sense of lightness as it emerges from the flat solar landscape. This results in a subtle addition to the skyline of turbines, enhancing both the visual aesthetics and experiential qualities of the energy landscape.

Det Kongelige Akademi understøtter FN’s verdensmål
Siden 2017 har Det Kongelige Akademi arbejdet med FN’s verdensmål. Det afspejler sig i forskning, undervisning og afgangsprojekter. Dette projekt har forholdt sig til følgende FN-mål