Off-The-Grid//Saur Village
Off-The-Grid//Saur Village is a self-sufficient energy housing community located in Dhun, Jaipur that aims to alleviate the social boundaries among socioeconomic groups by providing equal energy access through solar power. This architectural proposal responds to power challenges faced in India, exploring the possibilities of integrating solar panels within the architecture.
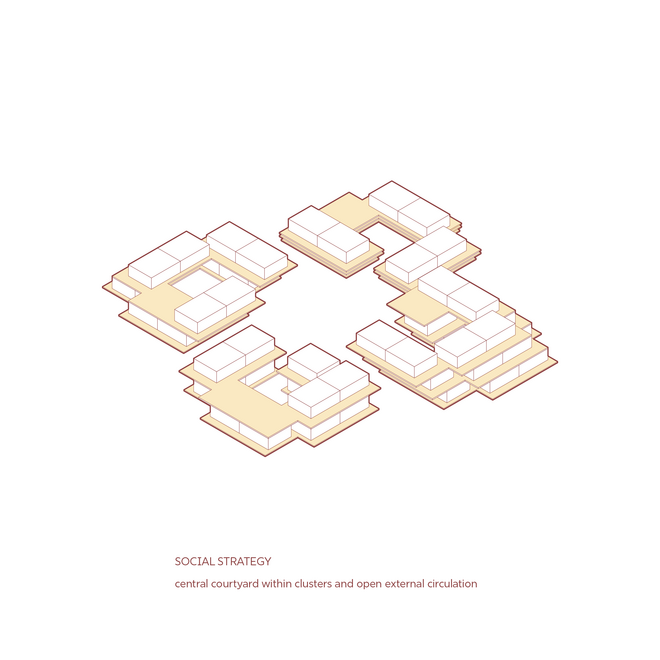
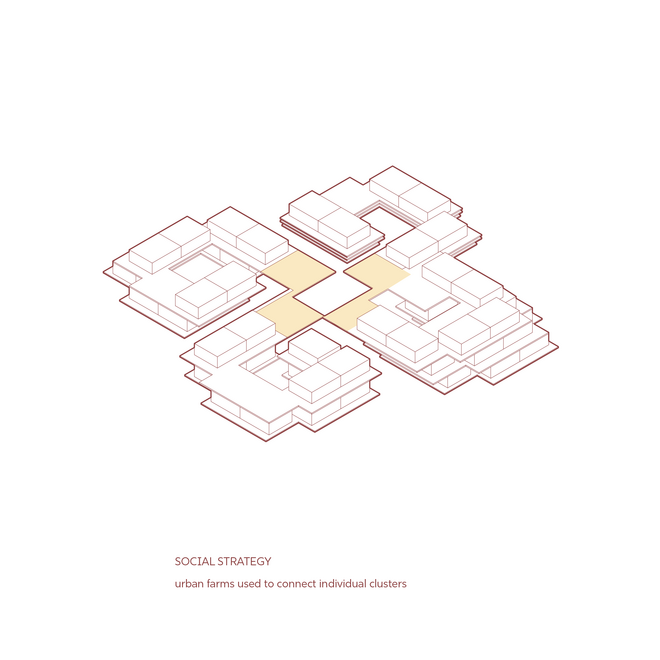
The primary aim of this project was to investigate social inclusivity within the housing community, explore the integration of solar farms into the architecture, and utilise urban farming to bridge residential and industrial spaces.
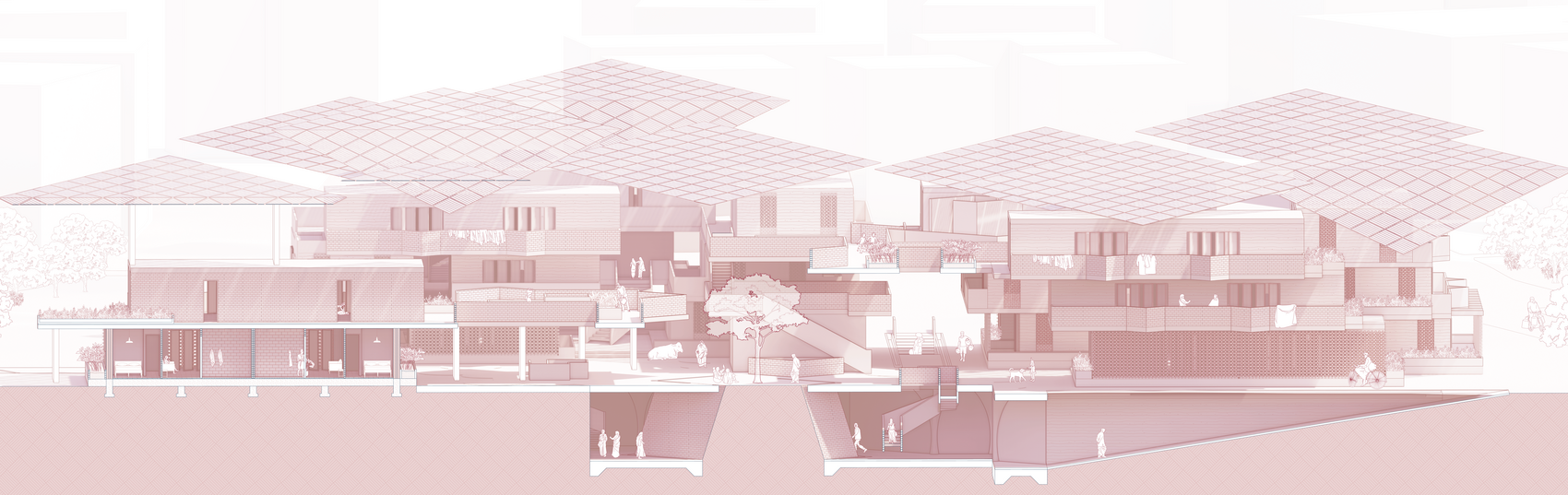
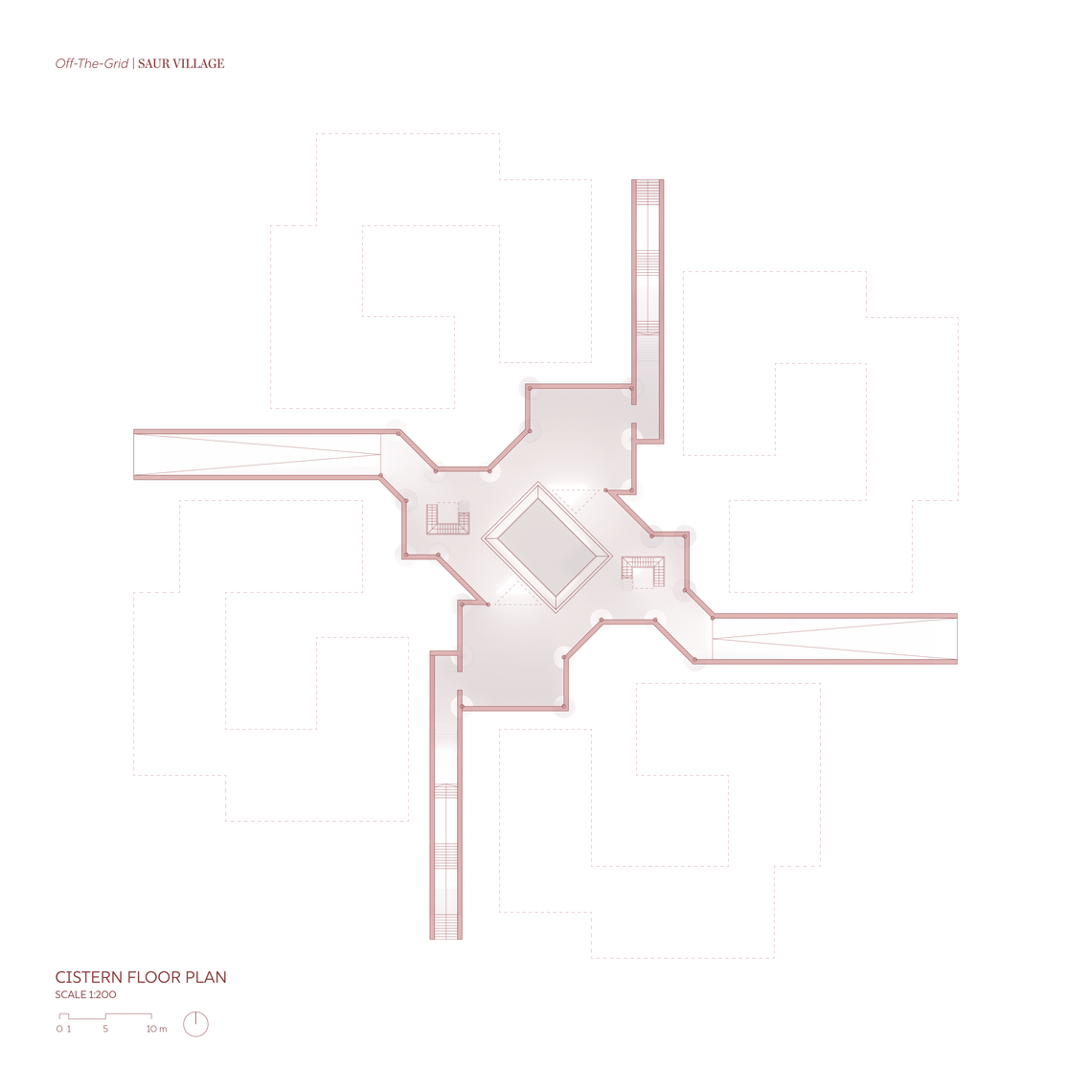
The Off-The-Grid//Saur Village community comprises three main components: the housing community, urban farming, and energy production through solar panels. Urban farming serves as the link between housing and energy production, providing a social space for shared gardening while enhancing solar panel efficiency through agrivoltaics. An underground cistern was introduced to manage site flooding during the monsoon season, with the collected water used for irrigating the urban farm. Excess energy generated is stored in sand batteries, ensuring a reliable power supply during the reduced sunlight hours of the monsoon season.
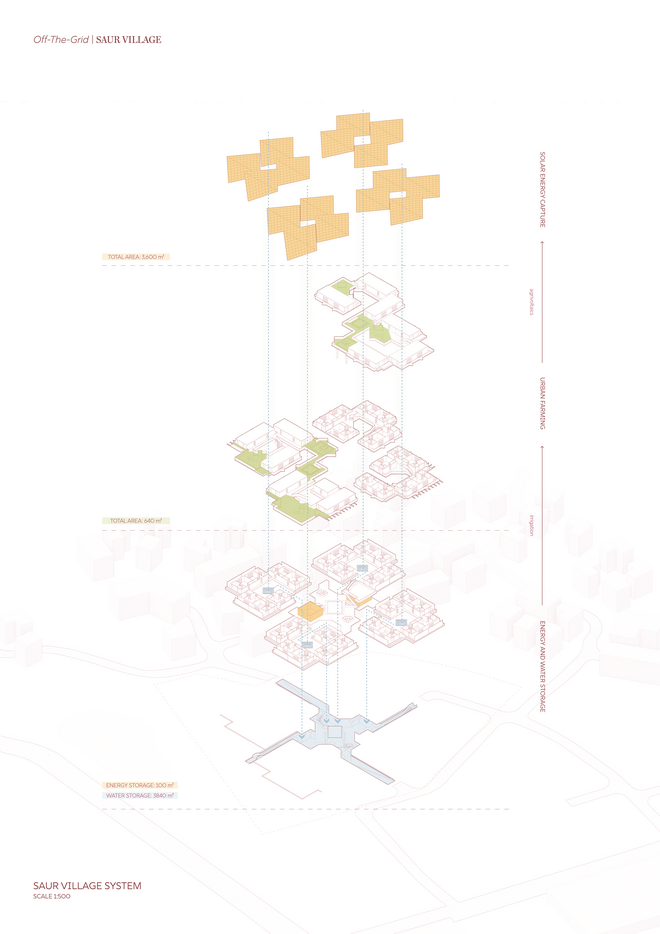
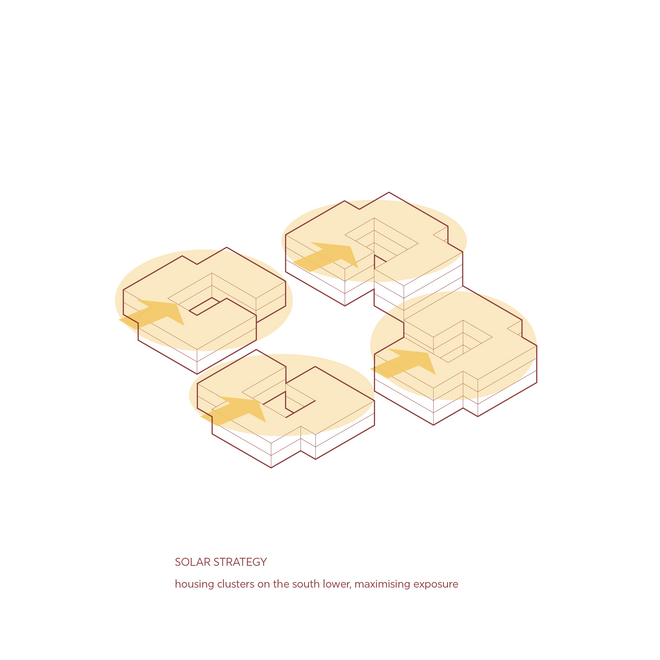
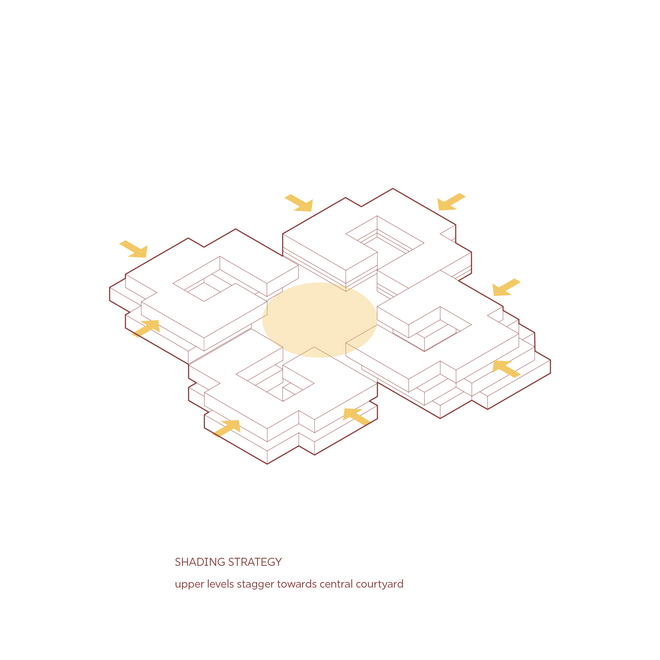
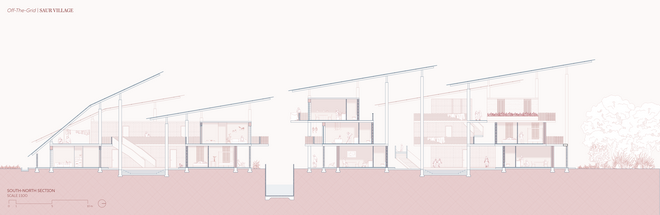
Given the importance of shade in this context, while also requiring maximum solar radiation exposure for optimal sunlight capture, the building and solar panels are designed to work in harmony, both providing shade and receiving sunlight. This is achieved by staggering the buildings towards the central courtyard, which enhances shading and creates a comfortable outdoor space for residents. A semi-transparent solar roof canopy, designed using incident radiation and PV placement simulations to determine its form and tilt angles, adds extra shading throughout the day. Additionally, the canopy directs rainwater into the cistern, facilitating annual cleaning during the monsoon season.
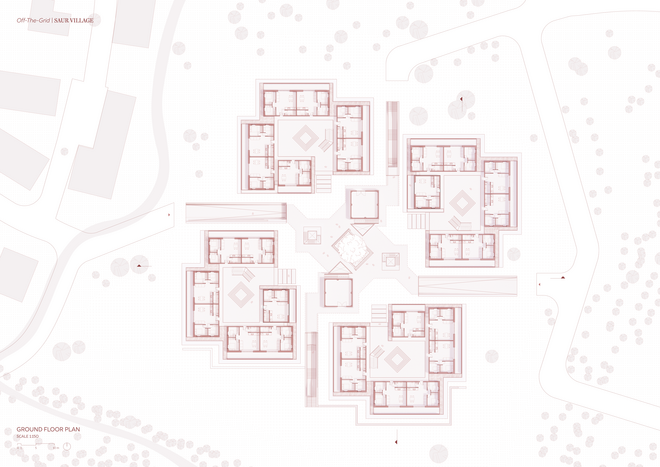
Ground Floor Plan
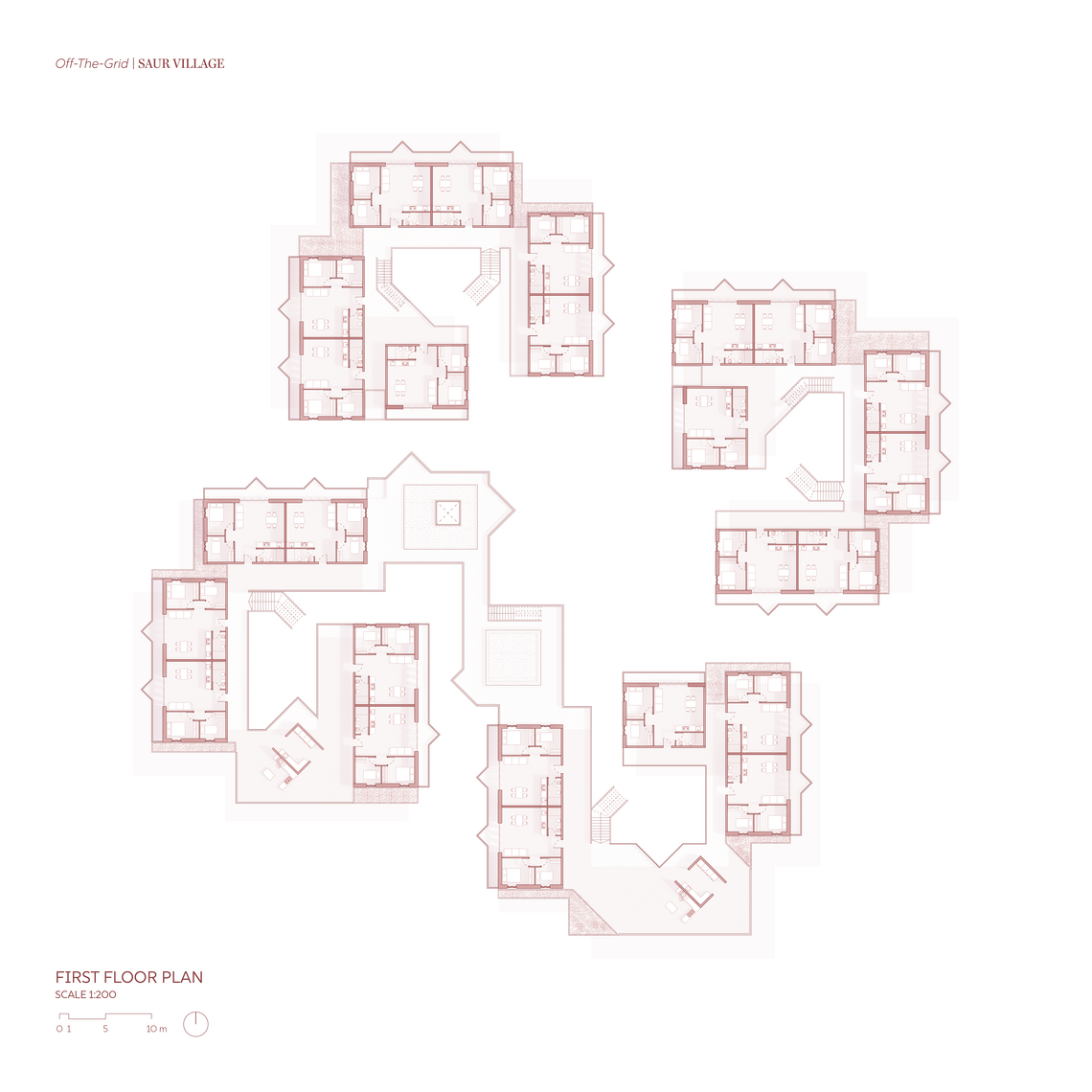
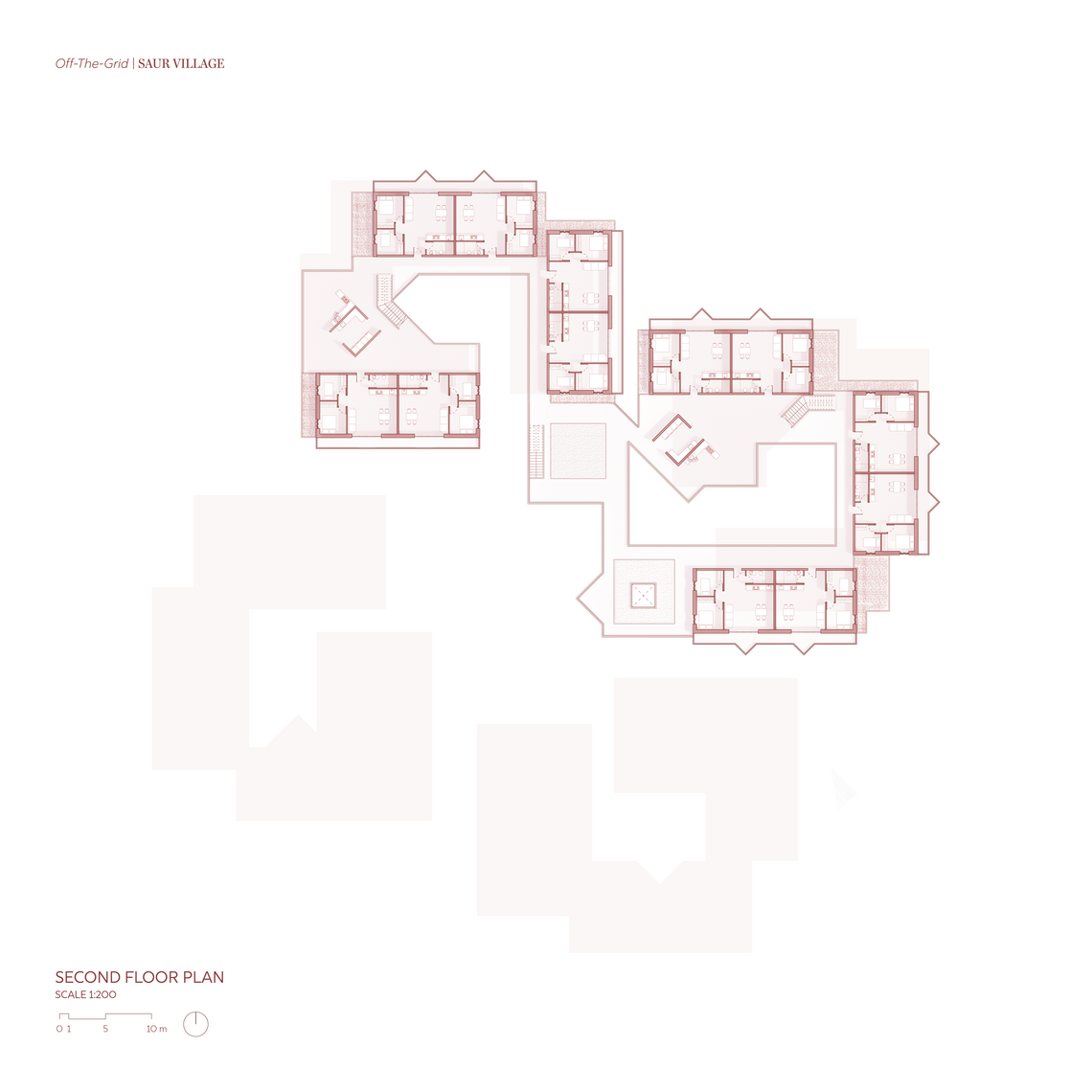
Floor Plans
Det Kongelige Akademi understøtter FN’s verdensmål
Siden 2017 har Det Kongelige Akademi arbejdet med FN’s verdensmål. Det afspejler sig i forskning, undervisning og afgangsprojekter. Dette projekt har forholdt sig til følgende FN-mål