Wood Hybrids – Thermal III

The project investigates, examines, and propose a wood-textile thermal-active structure that directly address questions on reducing embodied and operational energy in the built environment by a novel use of CO2 absorbing regenerative materials. This means to develop, study and test thermal form-active composites, based on Oak-Paulownia-Flax materials. The intention is to understand and be able to compose the material composite structure for articulated thermal responsive behaviours at the architectural scale of form-active elements.
Three studies are combined into forming the self-bearing thermally responsive structure, 1) the temperature-driven form-active elements, 2) the layering of materials for insulation properties and 3) the loadbearing structural system that hosts the thermal-active elements.
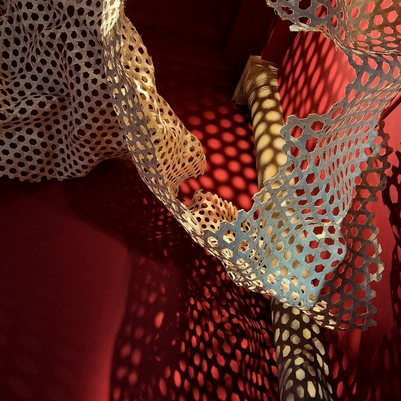
Combining the three materials of oak-paulownia-flax as a composite provides unique characteristics, with high thermal expansion of Oak, low thermal expansion and high dimensional stability of Paulownia, and layered, flexible properties of flax textiles.


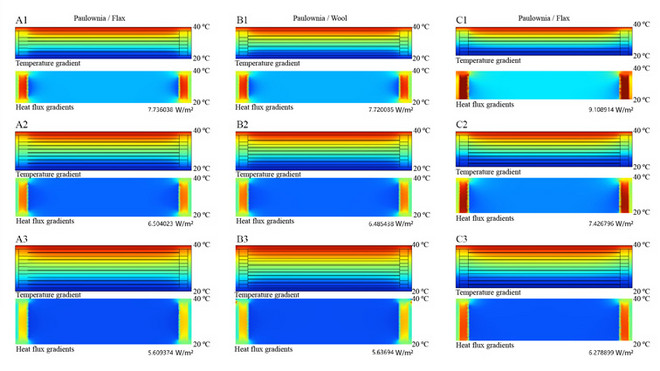
Together, the thermal-active wood bi-layers are combined with flex textiles to create a responsive and modular envelope element, with insulation properties defined by the number of layers of the module. To understand layered composites’ abilities to insulate and transfer heat, thermal simulations are conducted with varied material combinations and textile layer numbers.
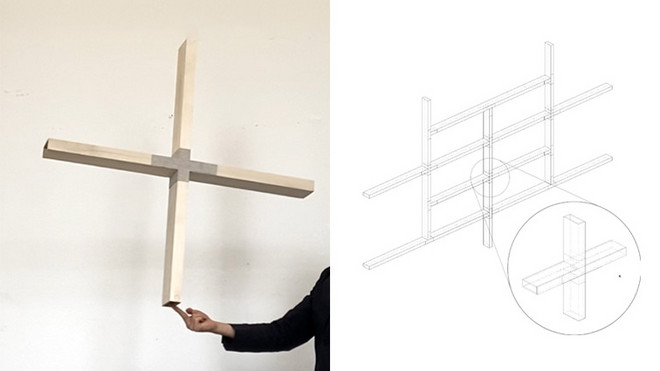
As a structural system hosting the thermal response modules developed, a new lightweight load-bearing BoxBeam-Zollinger structure, with flax textile surface connections, is proposed. Both form-active composite and load-bearing structures are inspired by skin-on-frame material-structural concepts observed in Inuit vernacular boat cultures. The structure alone is measured to 1 kg/m2, with a combined weight of the entire responsive envelope of 4.3 kg/m2.
The three investigations are combined into a full-scale demonstrator study as physical and computational for observation and simulation analysis.



Funding
The research has been funded by the Realdania Foundation and the Obel Family Foundation as part of the ‘Thermal Adaptive Architecture’ project.
Dissemination
Foged, IW 2022, 'A wood-textile thermal active architectural envelope', in: Architecture, Structures and Construction. Read it here